[ad_1]
• Characteristic Story • seventy fifth Anniversary
At a Look:
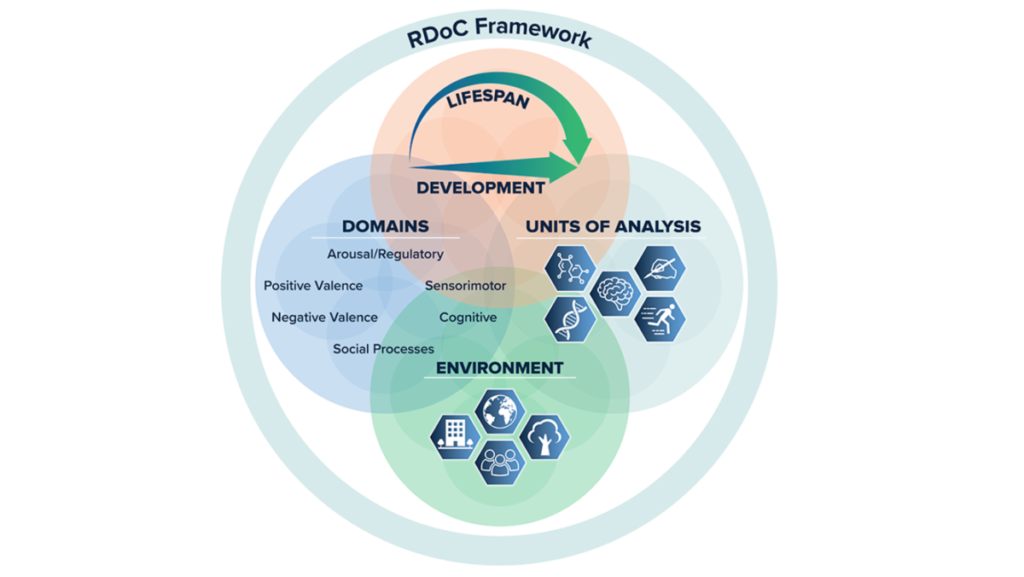
- The Analysis Area Standards framework (RDoC) was created in 2010 by the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being.
- The framework encourages researchers to look at useful processes which can be carried out by the mind on a continuum from regular to irregular.
- This fashion of researching psychological issues may help overcome inherent limitations in utilizing all-or-nothing diagnostic methods for analysis.
- Researchers worldwide have taken up the rules of RDoC.
- The framework continues to evolve and replace as new data turns into out there.
President George H. W. Bush proclaimed the Nineteen Nineties “The Decade of the Mind ,” urging the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being (NIMH), and others to lift consciousness about the advantages of mind analysis.
“Over time, our understanding of the mind—the way it works, what goes flawed when it’s injured or diseased—has elevated dramatically. Nevertheless, we nonetheless have rather more to study,” learn the president’s proclamation. “The necessity for continued research of the mind is compelling: tens of millions of Individuals are affected every year by issues of the mind…Right now, these people and their households are justifiably hopeful, for a brand new period of discovery is dawning in mind analysis.”
Nonetheless, regardless of the explosion of recent methods and instruments for finding out the mind, equivalent to useful magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), many psychological well being researchers have been rising annoyed that their area was not progressing as shortly as they’d hoped.
For many years, researchers have studied psychological issues utilizing diagnoses based mostly on the Diagnostic and Statistical Handbook of Psychological Problems (DSM)—a handbook that lists the signs of psychological issues and the standards for diagnosing an individual with a dysfunction. However, amongst many researchers, suspicion was rising that the system used to diagnose psychological issues is probably not the easiest way to review them.
“There are a lot of advantages to utilizing the DSM in medical settings—it gives reliability and ease of analysis. It additionally gives a clear-cut analysis for sufferers, which may be essential to request insurance-based protection of healthcare or job- or school-based lodging,” mentioned Bruce Cuthbert, Ph.D., who headed the workgroup that developed NIMH’s Analysis Area Standards Initiative. “Nevertheless, when utilized in analysis, this strategy is just not all the time preferrred.”
Researchers would usually take a look at individuals with a particular identified DSM dysfunction towards these with a distinct dysfunction or with no dysfunction and see how the teams differed. Nevertheless, completely different psychological issues can have related signs, and folks may be identified with a number of completely different issues concurrently. As well as, a analysis utilizing the DSM is all or none—sufferers both qualify for the dysfunction based mostly on their variety of signs, or they don’t. This black-and-white strategy means there could also be individuals who expertise signs of a psychological dysfunction however simply miss the cutoff for analysis.
Dr. Cuthbert, who’s now the senior member of the RDoC Unit which orchestrates RDoC work, said that “Diagnostic methods are based mostly on medical indicators and signs, however indicators and signs can’t actually inform us a lot about what’s going on within the mind or the underlying causes of a dysfunction. With trendy neuroscience, we have been seeing that data on genetic, pathophysiological, and psychological causes of psychological issues didn’t line up properly with the present diagnostic dysfunction classes, suggesting that there have been central processes that relate to psychological issues that weren’t being mirrored in DMS-based analysis.”
Highway to evolution
Involved concerning the limits of utilizing the DSM for analysis, Dr. Cuthbert, a professor of medical psychology on the College of Minnesota on the time, approached Dr. Thomas Insel (then NIMH director) throughout a convention within the autumn of 2008. Dr. Cuthbert recalled saying, “I believe it’s actually essential that we begin dimensions of features associated to psychological issues equivalent to concern, working reminiscence, and reward methods as a result of we all know that these dimensions reduce throughout varied issues. I believe NIMH actually wants to consider psychological issues on this new manner.”
Dr. Cuthbert didn’t understand it then, however he was suggesting one thing much like concepts that NIMH was contemplating. Simply months earlier, Dr. Insel had spearheaded the inclusion of a aim in NIMH’s 2008 Strategic Plan for Analysis to “develop, for analysis functions, new methods of classifying psychological issues based mostly on dimensions of observable conduct and neurobiological measures.”
Unaware of the brand new strategic aim, Dr. Cuthbert was stunned when Dr. Insel’s senior advisor, Marlene Guzman, known as a couple of weeks later to ask if he’d be fascinated by taking a sabbatical to assist lead this new effort. Dr. Cuthbert quickly transitioned right into a full-time NIMH worker, becoming a member of the Institute at an thrilling time to steer the event of what grew to become often called the Analysis Area Standards (RDoC) Framework. The hassle started in 2009 with the creation of an inside working group of interdisciplinary NIMH employees who recognized core useful areas that may very well be used as examples of what analysis utilizing this new conceptual framework seemed like.
The workgroup members conceived a daring change in how investigators studied psychological issues.
“We needed researchers to transition from psychological issues as all or none diagnoses based mostly on teams of signs. As a substitute, we needed to encourage researchers to grasp how fundamental core features of the mind—like concern processing and reward processing—work at a organic and behavioral stage and the way these core features contribute to psychological issues,” mentioned Dr. Cuthbert.
This strategy would incorporate organic and behavioral measures of psychological issues and study processes that reduce throughout and apply to all psychological issues. From Dr. Cuthbert’s standpoint, this might assist treatment among the frustrations psychological well being researchers have been experiencing.
Across the identical time the workgroup was sharing its plans and organizing the primary steps, Sarah Morris, Ph.D., was a researcher specializing in schizophrenia on the College of Maryland Faculty of Medication in Baltimore. When she first learn these papers, she questioned what this new strategy would imply for her analysis, her grants, and her lab.
She additionally remembered feeling that this new strategy mirrored what she was seeing in her information.
“After I grouped my individuals by these with and with out schizophrenia, there was quite a lot of overlap, and there was quite a lot of variability throughout the board, and so it felt like RDoC offered the pathway ahead to dissect that and kind it out,” mentioned Dr. Morris.
Later that yr, Dr. Morris joined NIMH and the RDoC workgroup, saying, “I used to be bumping up towards a wall day-after-day in my very own work and within the information in entrance of me. And the concept that somebody would give the sector permission to strive one thing new—that was tremendous thrilling.”
The 5 unique RDoC domains of functioning have been launched to the broader scientific neighborhood in a sequence of articles revealed in 2010 .
To ascertain the brand new framework, the RDoC workgroup (together with Drs. Cuthbert and Morris) started a sequence of workshops in 2011 to gather suggestions from specialists in varied areas from the bigger scientific neighborhood. 5 workshops have been held over the subsequent two years, every with a distinct broad area of functioning based mostly upon prior fundamental behavioral neuroscience. The 5 domains have been known as:
- Unfavourable valence (which included processes associated to issues like concern, menace, and loss)
- Constructive valence (which included processes associated to working for rewards and appreciating rewards)
- Cognitive processes
- Social processes
- Arousal and regulation processes (together with arousal methods for the physique and sleep).
At every workshop, specialists outlined a number of particular features, termed constructs, that fell inside the area of curiosity. For example, constructs within the cognitive processes area included consideration, reminiscence, cognitive management, and others.
The results of these suggestions classes was a framework that described psychological issues because the interplay between completely different useful processes—processes that might happen on a continuum from regular to irregular. Researchers may measure these useful processes in a wide range of complementary methods—for instance, by genes related to these processes, the mind circuits that implement these processes, assessments or observations of behaviors that signify these useful processes, and what sufferers report about their considerations. Additionally included within the framework was an understanding that useful processes related to psychological issues are impacted and altered by the atmosphere and an individual’s developmental stage.
Preserving momentum
Over time, the Framework continued evolving and adapting to the altering science. In 2018, a sixth useful space known as sensorimotor processes was added to the Framework, and in 2019, a workshop was held to raised incorporate developmental and environmental processes into the framework.;
Since its creation, the usage of RDoC rules in psychological well being analysis has unfold throughout the U.S. and the remainder of the world. For instance, the Psychiatric Rankings utilizing Intermediate Stratified Markers undertaking (PRISM) , which receives funding from the European Union’s Modern Medicines Initiative, is looking for to hyperlink organic markers of social withdrawal with medical diagnoses utilizing RDoC-style rules. Equally, the Roadmap for Psychological Well being Analysis in Europe (ROAMER) undertaking by the European Fee sought to combine psychological well being analysis throughout Europe utilizing rules much like these within the RDoC Framework.;
Dr. Morris, who has acceded to the Head of the RDoC Unit, commented: “The truth that investigators and science funders exterior the USA are additionally pursuing related approaches offers me confidence that we’ve been on the precise pathway. I simply assume that this has acquired to be how nature works and that we’re in higher alignment with the fundamental basic processes which can be of curiosity to understanding psychological issues.”
The RDoC framework will proceed to adapt and alter with rising science to stay related as a useful resource for researchers now and sooner or later. For example, NIMH continues to work towards the event and optimization of instruments to evaluate RDoC constructs and helps data-driven efforts to measure perform inside and throughout domains.
“For the tens of millions of individuals impacted by psychological issues, analysis means hope. The RDoC framework helps us research psychological issues differently and has already pushed appreciable change within the area over the previous decade,” mentioned Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., director of NIMH. “We hope this and different progressive approaches will proceed to speed up analysis progress, paving the way in which for prevention, restoration, and treatment.”
Publications
Cuthbert, B. N., & Insel, T. R. (2013). Towards the way forward for psychiatric analysis: The seven pillars of RDoC. BMC Medication, 11, 126. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-126
Cuthbert B. N. (2014). Translating intermediate phenotypes to psychopathology: The NIMH Analysis Area Standards. Psychophysiology, 51(12), 1205–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12342
Cuthbert, B., & Insel, T. (2010). The info of analysis: New approaches to psychiatric classification. Psychiatry, 73(4), 311–314. https://doi.org/10.1521/psyc.2010.73.4.311
Cuthbert, B. N., & Kozak, M. J. (2013). Developing constructs for psychopathology: The NIMH analysis area standards. Journal of Irregular Psychology, 122(3), 928–937. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034028
Garvey, M. A., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2017). Growing a motor methods area for the NIMH RDoC program. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43(5), 935–936. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbx095
Insel, T. (2013). Remodeling analysis. http://www.nimh.nih.gov/about/director/2013/transforming-diagnosis.shtml
Kozak, M. J., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2016). The NIMH Analysis Area Standards initiative: Background, points, and pragmatics. Psychophysiology, 53(3), 286–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12518
Morris, S. E., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2012). Analysis Area Standards: Cognitive methods, neural circuits, and dimensions of conduct. Dialogues in Scientific Neuroscience, 14(1), 29–37. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2012.14.1/smorris
Sanislow, C. A., Pine, D. S., Quinn, Ok. J., Kozak, M. J., Garvey, M. A., Heinssen, R. Ok., Wang, P. S., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2010). Growing constructs for psychopathology analysis: Analysis area standards. Journal of Irregular Psychology, 119(4), 631–639. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020909
Be taught extra
[ad_2]